|
|
The Amazon: The World's Largest Rainforest
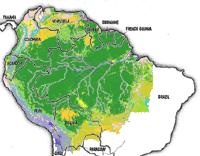
The Amazon River Basin is home to the largest rainforest on Earth. The basin -- roughly the size of the forty-eight contiguous United States -- covers some 40% of the South American continent and includes parts of eight South American countries: Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, and Suriname.
Reflecting environmental conditions as well as past human influence, the Amazon is made up of a mosaic of ecosystems and vegetation types including rainforests, seasonal forests, deciduous forests, flooded forests, and savannas. The basin is drained by the Amazon River, the world's largest river in terms of discharge, and the second longest river in the world after the Nile. The river is made up of over 1,100 tributaries, 17 of which are longer than 1000 miles, and two of which (the Negro and the Madeira) are larger, in terms of volume, than the Zaire river. The river system is the lifeline of the forest and its history plays an important part in the development of its rainforests.
HISTORY
At one time Amazon River flowed westward, perhaps as part of a proto-Congo (Zaire) river system from the interior of present day Africa when the continents were joined as part of Gondwana. Fifteen million years ago, the Andes were formed by the collision of the South American plate with the Nazca plate. The rise of the Andes and the linkage of the Brazilian and Guyana bedrock shields, blocked the river and caused the Amazon to become a vast inland sea. Gradually this inland sea became a massive swampy, freshwater lake and the marine inhabitants adapted to life in freshwater. For example, over 20 species of stingray, most closely related to those found in the Pacific Ocean, can be found today in the freshwaters of the Amazon.
About ten million years ago, waters worked through the sandstone to the west and the Amazon began to flow eastward. At this time the Amazon rainforest was born. During the Ice Age, sea levels dropped and the great Amazon lake rapidly drained and became a river. Three million years later, the ocean level receded enough to expose the Central American isthmus and allow mass migration of mammal species between the Americas.
The Ice Ages caused tropical rainforest around the world to retreat. Although debated, it is believed that much of the Amazon reverted to savanna and montane forest (see chapter 3-Ice Ages and Glaciation). Savanna divided patches of rainforest into "islands" and separated existing species for periods long enough to allow genetic differentiation (a similar rainforest retreat took place in Africa. Delta core samples suggest that even the mighty Congo watershed was void of rainforest at this time). When the ice ages ended, the forest was again joined and the species that were once one had diverged significantly enough to be constitute designation as separate species, adding to the tremendous diversity of the region. About 6000 years ago, sea levels rose about 130 meters, once again causing the river to be inundated like a long, giant freshwater lake.
THE AMAZON RIVER TODAY
How large is the Amazon rainforest?
In Brazil, the Amazon covers surface area of 4,005,082 square kilometers. In total, the Amazon River drains about 6,915,000 square kilometers (2,722,000 square miles), or roughly 40 percent of South America. For comparison, the land area of the United States (including Alaska and Hawaii) is 9,629,091 square kilometers.
|
|
Today the Amazon River is the most voluminous river on Earth, eleven times the volume of the Mississippi, and drains an area equivalent in size to the United States. During the high water season, the river's mouth may be 300 miles wide and every day up to 500 billion cubic feet of water (5,787,037 cubic feet/sec) flow into the Atlantic. For reference, the Amazon's daily freshwater discharge into the Atlantic is enough to supply New York City's freshwater needs for nine years. The force of the current -- from sheer water volume alone -- causes Amazon River water to continue flowing 125 miles out to sea before mixing with Atlantic salt water. Early sailors could drink freshwater out of the ocean before sighting the South American continent.
The river current carries tons of suspended sediment all the way from the Andes and gives the river a characteristic muddy whitewater appearance. It is calculated that 106 million cubic feet of suspended sediment are swept into the ocean each day. The result from the silt deposited at the mouth of the Amazon is Majaro island, a river island about the size of Switzerland.
THE AMAZON RAINFOREST
|
|
For kids
Multi-media
|
|
|
|
|
THE AMAZON
ADVERTISEMENT
KEY ARTICLES
RAINFORESTS

ADVERTISEMENT
FOR KIDS

MONGABAY.COM


Share
|